
Benefits of Metal Forging
CNC metal forging delivers superior precision, strength, and efficiency. With advanced technology, it ensures consistent quality, tight tolerances, and minimal waste, resulting in cost savings and sustainability. Its versatility in shaping complex components makes it a top choice across industries for enhancing performance and reducing production costs.
Types of CNC Forging
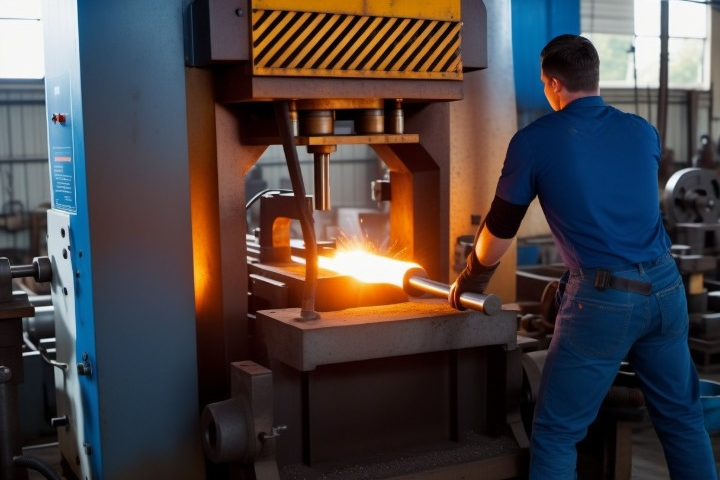

Hammer or Smith Forging

Drop Hammer Forging

Press Forging

Upset Forging

Roll Forging
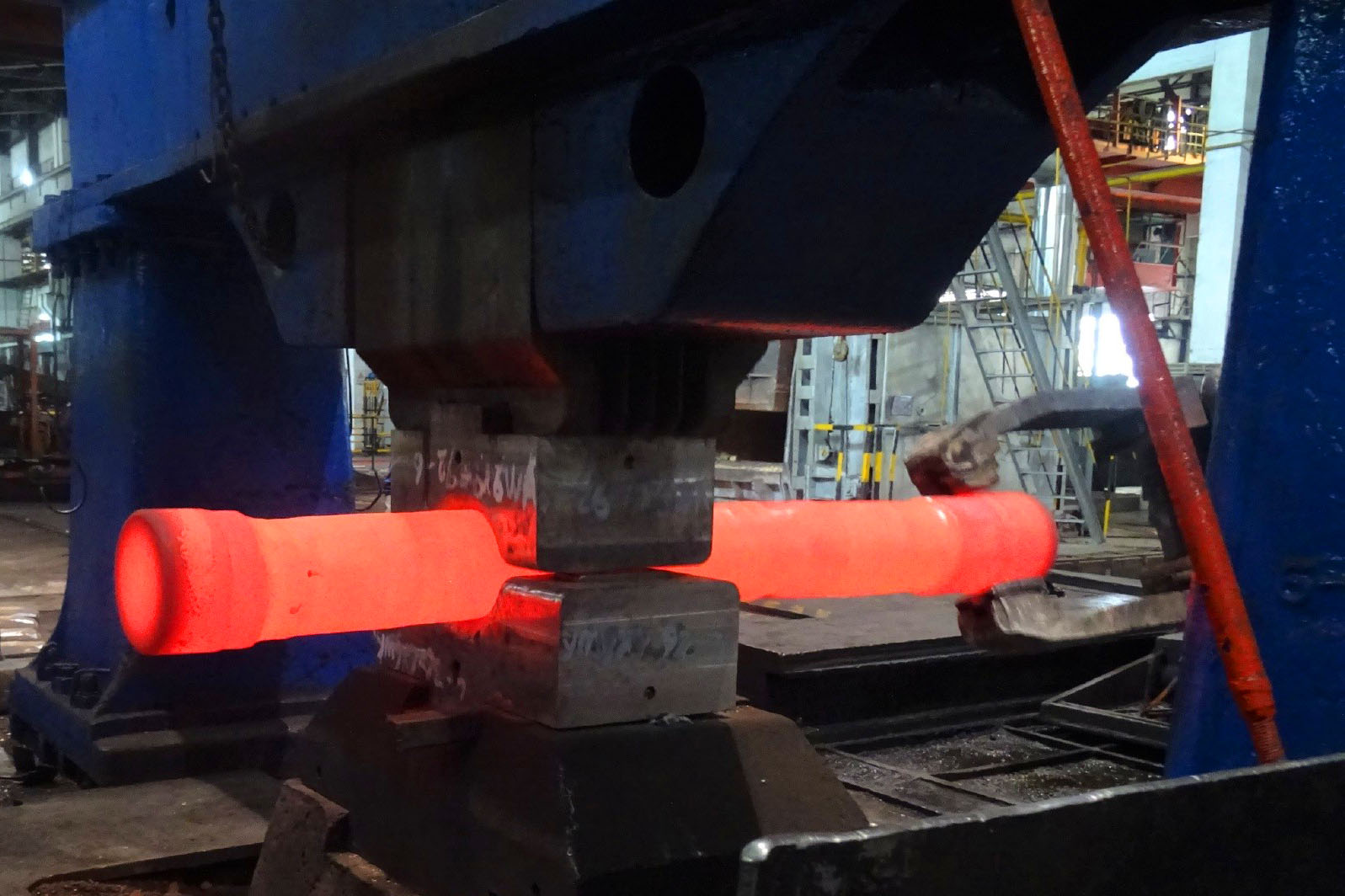
Open Die Forging
Open die forging, also known as free forging, involves shaping metal between flat dies that do not completely enclose the workpiece. This method allows for flexibility in shaping large and complex metal components while retaining the benefits of forging, such as improved mechanical properties and grain structure refinement.

Metal Forging Materials
- Aluminum Alloy
- Carbon Steel
- Copper Alloy
- Nickel Alloy
- Tungsten Alloy
- Titanium Alloy
Applied Industries

Aviation
Forged components such as turbine discs, hollow shafts, blades, wing beams, fuselage ribs, wheel hubs, and inner and outer cylinder bodies of landing gear are critical for aircraft safety. Aircraft components are mostly made from high-strength, wear-resistant, and corrosion-resistant materials such as aluminum alloys, titanium alloys, and nickel-based alloys.

Automotive Industry
Forged components include crankshafts, connecting rods, camshafts for automobile engines, front beams, steering knuckles for front axles, half shafts, half shaft sleeves, and transmission gears in the axle housing.

Maritime Industry
Marine forgings are divided into three main categories: engine forgings, shaft system forgings, and rudder system forgings. Engine forgings are similar to diesel engine forgings. Shaft system forgings include thrust shafts, intermediate shafts, and stern shafts. Rudder system forgings include rudder stocks, rudder posts, and rudder pins.

Military
Forged products are extensively used in military equipment, including gun barrels, muzzle brakes, and gun tails for cannons; rifled barrels and bayonets for infantry weapons; rocket launchers and fixed seats for submarine depth charges; stainless steel valve bodies for high-pressure coolers in nuclear submarines; and shells and bullets.
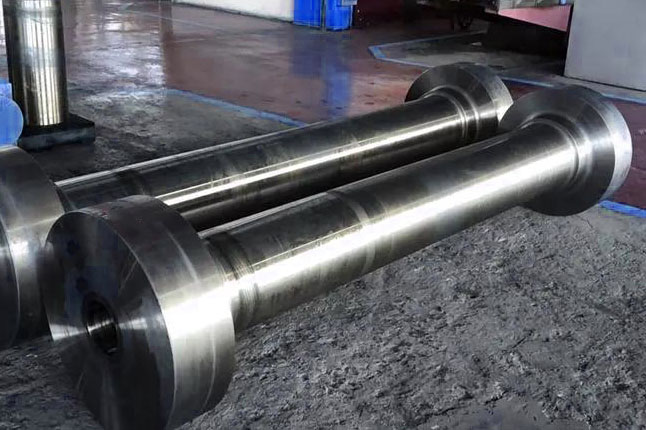

Petrochemical
Forged components find wide applications in petrochemical equipment, such as manholes and flanges for spherical tanks, various tube sheets and welded flanges for heat exchangers, integral forging cylinders (pressure vessels) for catalytic cracking reactors, cylinder sections for hydrogen reactors, and top covers, bottom covers, and heads for fertilizer equipment.

Mining Equipment
Forged components are used in mining equipment, hoisting equipment, crushing equipment, grinding equipment, beneficiation equipment, sintering equipment, and nuclear power forgings.
CNC Forging Vs Casting Vs Machining
| Key Points | CNC Machining | CNC Casting | CNC Forging |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cost | High cost, skilled | High cost, skilled | Lower cost, no skilled |
| Operator Requirement | Skilled | Skilled | No specialized |
| Processing Time | Long, multiple steps | Long mold | Short, efficient |
| Programming | High skill | No need | No need |
| Setup Time | Long setup | Short setup | Short setup |
| Size Limitation | Limited, small batch | Less constrained | Less constrained |
| Production Efficiency | - | Mass production | High efficiency |
| Internal Defects | - | Internal defects | - |
| Scrap Rate | - | High scrap | - |
| Dimensional Accuracy | - | Lower accuracy | Higher accuracy |
| Mechanical Properties | - | Lower strength, toughness | Higher strength, toughness |
| Mold Lifespan | - | Short lifespan | - |
| Physical Consistency | - | Inconsistent | - |
Our Capabilities

Wherever you are, we can satisfy your requirement for certification.
We are able to produce Over 20000 forging parts per year.
We use the finest materials and top-notch craftsmanship to ensure products quality.
Choosing our forging service to save you 60% of the cost.
The lead time depends on your production scale, usually 3~5 days.
Products forged by us have low scrap rate, few defects, and a pass rate of 99%.
How to Work with Us?
Upload Your Project Files
Such as jpg, pdf, 3d files, we are committed to protecting your privacy.
Evaluation & Quotation
Our experts evaluate your project, and then quote back to you by email.
Confirm and Start Forging
If anything is ok, we can arrange production after the payment.
Ready to Manufacture CNC Forging Parts?
Just fill out the form below and upload the attachment to start.
